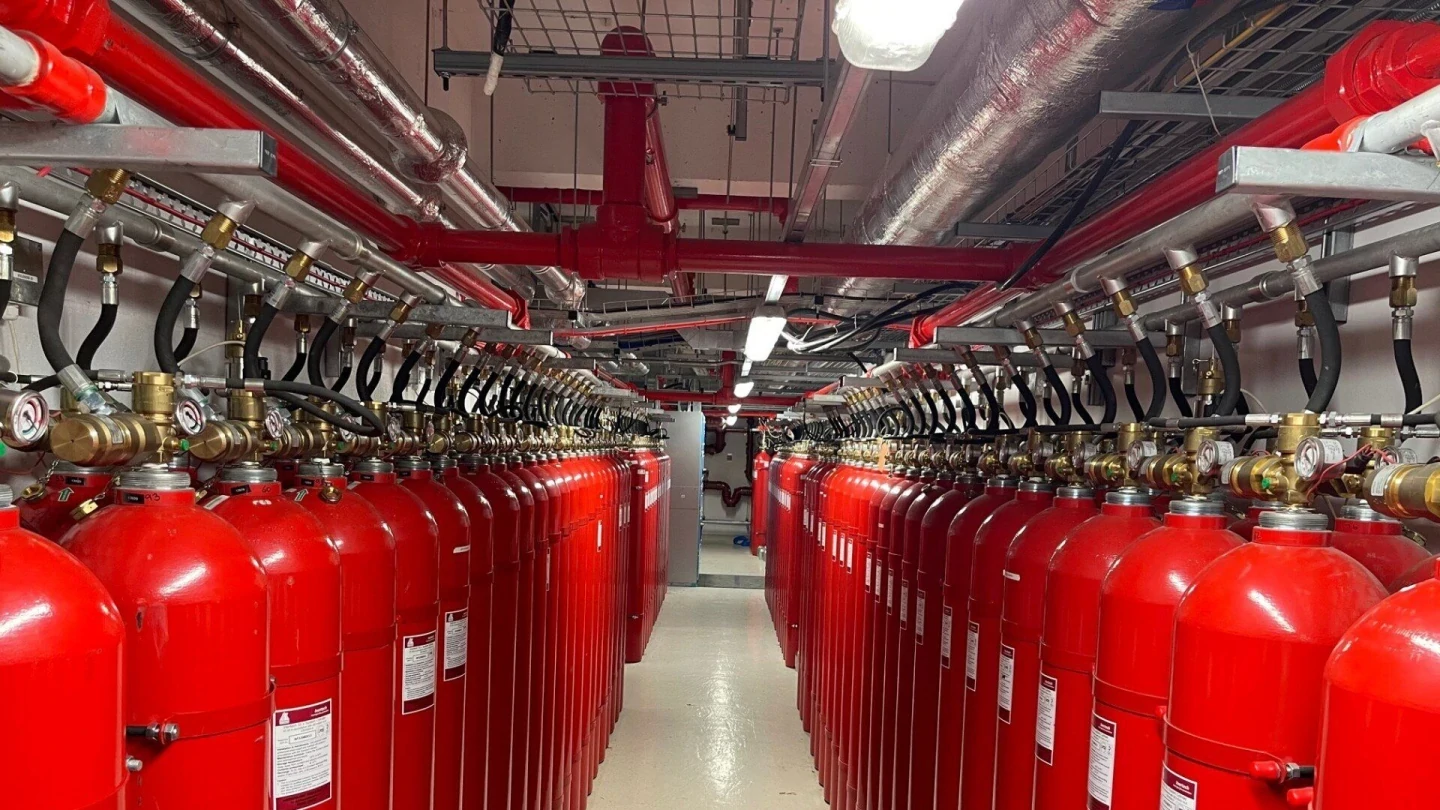
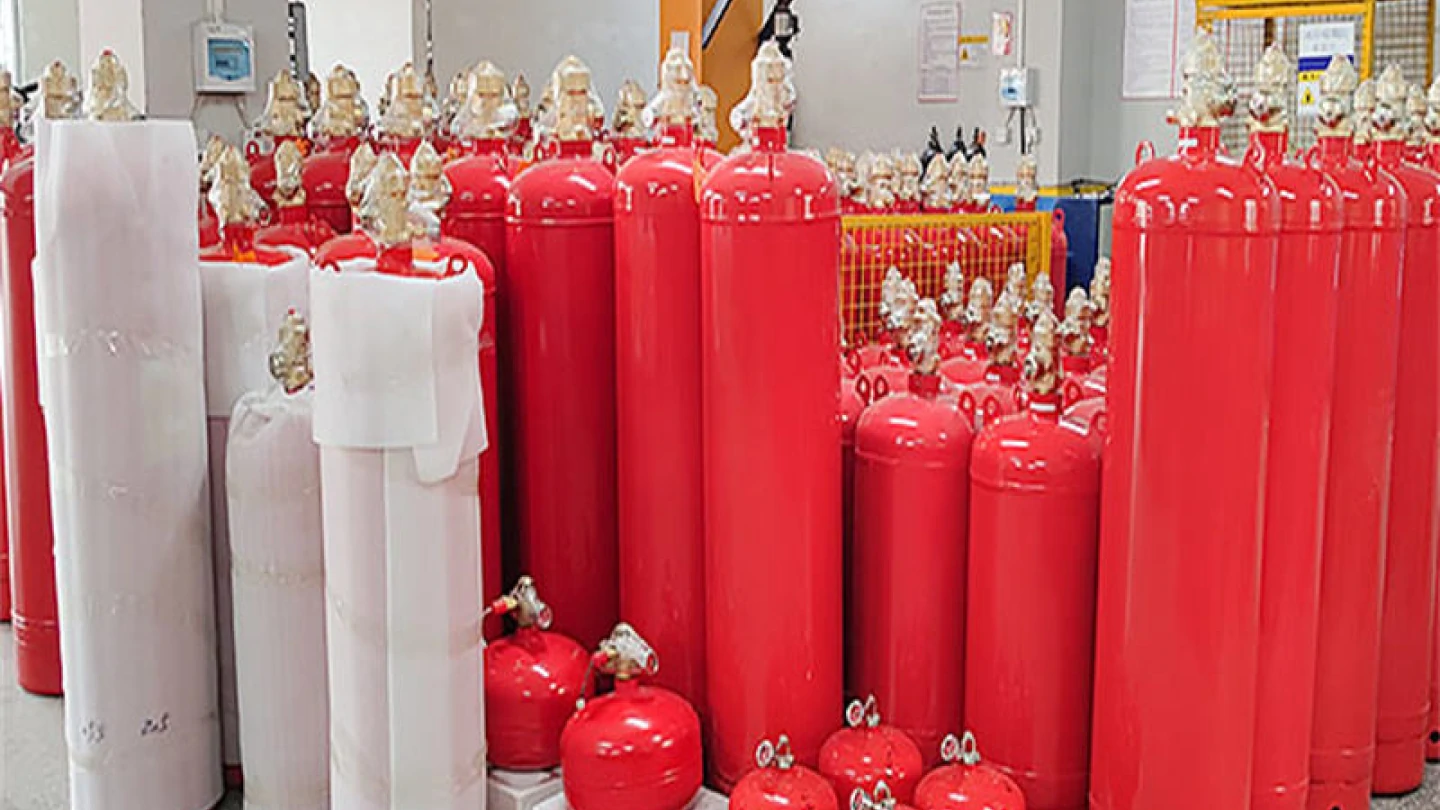
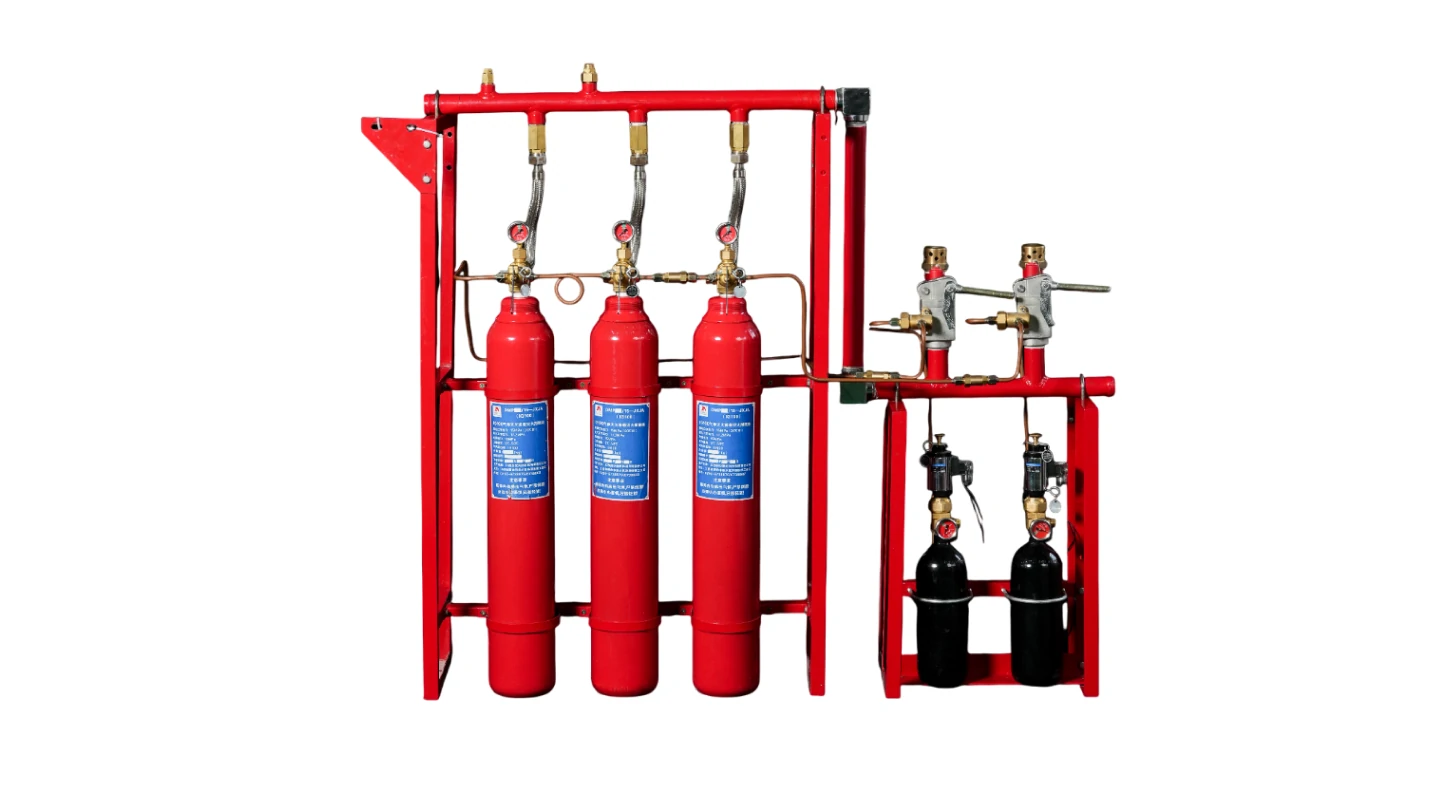
Fire, as a sudden disaster, poses a huge threat to human society. With the acceleration of urbanization and the continuous development of construction technology, fire safety issues are increasingly valued. Fire suppression system, as an important means of reducing fire losses and protecting the safety of people’s lives and property, are being studied and applied more and more widely. Now, please join us in discussing the definition of fire suppression systems, the working principles of fire suppression systems, the types of common fire suppression systems, and their roles in modern society with Firenix, a fire protection expert.
What is a fire suppresion system?
Fire suppression systems, defined from a professional standpoint, are an integrated assembly of equipment and procedures that incorporate the functions of detecting, suppressing, or extinguishing fires. Their operational modes include both automatic and manual types, achieving the goal of halting the spread of fires or directly terminating combustion reactions through a variety of specialized mechanisms.
Automatic fire suppression systems utilize advanced sensor technology and intelligent control units to automatically initiate a response at the moment a fire occurs. Manual fire suppression systems, on the other hand, rely on operators to judge the fire situation on-site and manually activate the starting device. Both play a crucial role in different application scenarios.
Fire suppression systems are an indispensable part of any fire protection infrastructure. “Fire extinguishing” refers to the collective term for any engineering unit aimed at extinguishing fires. It achieves the effect of extinguishing fires by using fire-extinguishing substances to disrupt any one of the three elements or the “fire triangle” of combustion. Common fire-extinguishing substances include water, foam, dry powder, CO2, and others.
How does a fire suppression system work?
Fire suppression systems are a set of complex safety mechanisms designed to detect and extinguish fires in their early stages in order to protect the safety of personnel and property. These systems consist of multiple key components, including control valves, piping, external alarms, nozzles, smoke detectors, flame detectors, fire indicator panels, fire brigade panels, fire sprinklers, and emergency alarm systems.
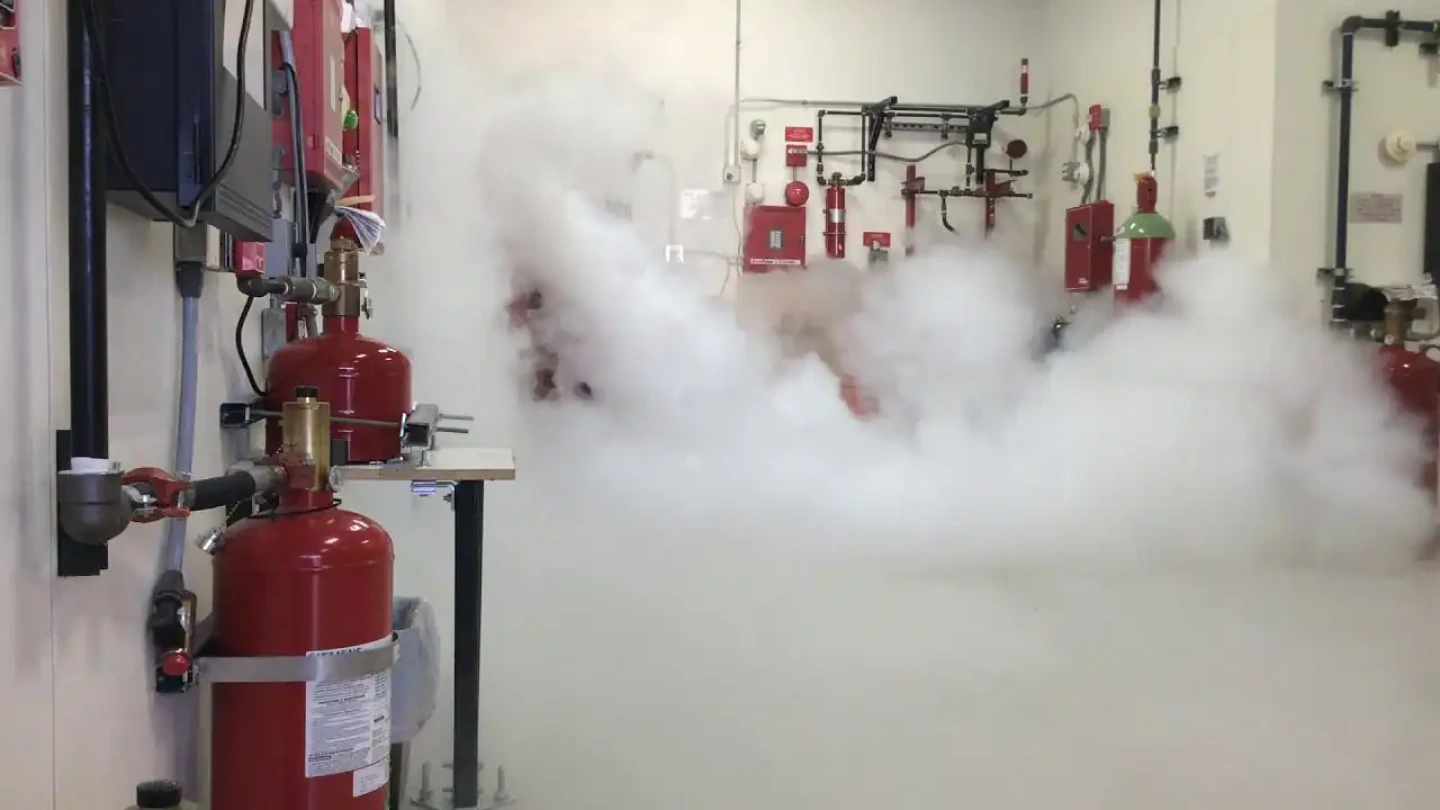

1.Fire Detection:
Fire detection, as the starting point of the fire suppression system operation, centers on the use of highly sensitive smoke detectors and flame detectors to accurately sense the smoke particles and thermal radiation signals released during the early stages of a fire. This process involves several professional procedures such as signal transmission, amplification, and processing to ensure that the system can respond accurately and reliably to fire signals.
2.System Activation:
Upon receiving a fire signal from the fire detection phase, the fire suppression system enters the activation phase according to the pre-set activation mode.
For automatic fire suppression systems, upon receiving a fire signal from the detectors, they instantly activate the starting device through the internal logic control circuitry, and simultaneously send signals to the associated control units and alarm systems, initiating a series of preparatory actions.
Manual fire suppression systems, on the other hand, require operators to manually operate the start button or switch after receiving a fire alarm and confirming the fire situation on-site. The subsequent action process is similar to that of the automatic system, but it is relatively slower in response speed, mainly depending on the accuracy and timeliness of human judgment and operation.
3. Suppressant Release
In the suppressant release phase, the fire suppression system precisely selects and releases the appropriate suppressant based on an accurate judgment of the fire type and its own design specifications. Common suppressants include water, gas, foam, or dry powder, which are transported through the piping system to nozzles or fire hoses.
4.Fire Extinguishing:
Different types of suppressants play unique and specialized roles in the fire extinguishing process. When water is used as a fire suppressant, it primarily extinguishes fires by its high specific heat capacity, absorbing a large amount of heat to cool the fire source. As it vaporizes, it isolates oxygen from the fuel, achieving the purpose of extinguishing the fire. Gaseous fire suppressants, such as carbon dioxide, work by diluting the air to a high concentration, significantly reducing the oxygen concentration in the combustion area to below the minimum required to sustain combustion. Some gaseous fire suppressants, like heptafluoropropane, can also interrupt the combustion chain reaction by chemically reacting with active free radicals in the combustion process, achieving the effect of extinguishing the fire.
Foam fire suppressants control and extinguish fires by forming a continuous, stable layer of foam on the surface of liquid fuels. This layer not only blocks the supply of oxygen but also absorbs heat through the evaporation of water within the foam, controlling and extinguishing the fire. Dry chemical fire suppressants work by rapidly decomposing into active groups when their powder particles come into contact with flames, combining with free radicals in the combustion reaction to suppress the chain reaction. At the same time, the powder covers the surface of the burning material, acting as an oxygen barrier and cooling agent, effectively curbing the spread of the fire.
5.Fire Alarm Systems and Warning Notifications:
Simultaneously with the activation of the fire suppression system, the associated fire alarm system is immediately activated.
The fire alarm system consists of multiple professional components, including fire detectors, alarm controllers, and alarm devices. When the detectors sense fire signals, they transmit the signals to the alarm controller. After processing and logical judgment of the signals, the alarm controller drives the alarm devices to emit strong audio and visual alarm signals, promptly warning the occupants or users of the building about the fire, guiding them to evacuate quickly to a safe area along predetermined evacuation routes.
Furthermore, advanced fire alarm systems have the capability to automatically send alarm information to the fire department. By connecting to the communication network of the fire command center, they can quickly convey critical information such as the specific location of the fire and the size of the blaze to the fire department. This allows fire professionals to arrive at the scene with professional equipment and carry out firefighting and rescue operations in the shortest possible time.
6.System Monitoring and Shutdown:
After initiating and carrying out fire extinguishing operations, the fire suppression system enters the system monitoring phase.During this phase, professional monitoring equipment such as temperature sensors and smoke detectors installed in the fire area continuously monitor key parameters such as temperature and smoke concentration in real-time to accurately determine if there are any remaining fire sources or smoke. When the monitoring data indicates that the fire has been successfully controlled and the environmental parameters have returned to normal ranges, the fire suppression system automatically shuts down the fire suppressant supply devices and related equipment according to the preset shutdown procedures, preventing excessive consumption of fire suppressants and waste of resources.
However, in some complex fire suppression systems, some components may remain in a specific working state or experience malfunctions after the system is activated. Professional technicians may need to manually reset and conduct a comprehensive check to ensure that all system components return to their initial normal state, preparing adequately for the next emergency fire response.
The design and implementation of a fire suppression system need to consider various factors, including building structure, fire risk assessment, and environmental conditions. An effective fire suppression system can respond quickly in the event of a fire, minimizing the damage caused by the fire and protecting the safety of personnel.
Fire suppression systems can be classified based on various factors. They can be divided into water, foam, gas, and chemical systems according to the type of suppressants used; classified into Class A, B, C, D, E, and F based on the types of fire hazards; and categorized into light hazard, medium hazard, and severe hazard classes based on fire severity. Special hazard systems also vary according to their modes of operation.
Some Main Classification Methods:
1.Classified Based on the Suppressant Used
Water:
Water, as a common and widely used fire suppressant, is primarily suitable for Class A fires involving solid materials based on its physical and chemical properties. However, for reactive metals like lithium and sodium that react violently with water or produce dangerous substances, water is not suitable to be used as a fire suppressant.
Foam:
Foam fire suppressants are specifically effective for Class B fires involving liquids. They are created by mixing foam concentrate, water, and air in precise proportions within specific foam-generating devices. When foam is sprayed onto the surface of liquid fuels such as gasoline and kerosene, it rapidly spreads and forms a continuous, stable, and relatively thick layer. This layer effectively isolates the liquid fuel from oxygen in the air, and the water content in the foam absorbs a significant amount of heat during evaporation, further reducing the surface temperature of the fuel and thus doubly suppressing the combustion reaction, preventing the spread and reignition of the fire. Different types of foam fire suppressants, such as protein foam, fluoroprotein foam, and film-forming foam, have varying fire extinguishing performance, anti-reignition capabilities, and applicable scenarios. In practical applications, they should be chosen based on specific fire conditions and environmental factors.
Gas:
Gas fire suppression systems commonly use fire suppressants like carbon dioxide and heptafluoropropane, which are mainly suitable for Class C fires involving gases and Class E fires involving electrical equipment due to their unique physical and chemical properties.
Carbon dioxide fire suppressant, with its inert gas characteristics, is stored under high pressure and rapidly fills the fire area upon release, significantly reducing the oxygen concentration and stopping combustion due to oxygen deprivation. Additionally, carbon dioxide absorbs a significant amount of heat during the release process, providing a cooling effect. Heptafluoropropane is a chemically synthesized gas fire suppressant, and its fire extinguishing mechanism is primarily based on chemical suppression. Within the fire area, the active free radicals produced by the decomposition of heptafluoropropane can quickly react with key active groups in the combustion reaction, interrupting the combustion chain reaction and efficiently extinguishing the fire.
In electrical fire scenarios, gas fire suppressants can effectively extinguish fires without damaging electrical equipment due to their non-conductive nature, avoiding the risk of secondary accidents such as short circuits that may be caused by water or foam fire suppressants. However, when using carbon dioxide fire suppressants, it is essential to fully consider their asphyxiation hazard to personnel and ensure their use after evacuation or in unoccupied areas.
Chemicals:
Dry chemical fire extinguishing agents, as a type of chemical fire suppressant, have a wide range of applicability and can effectively respond to various types of fires, including liquid, gas, and electrical fires. They are primarily composed of active fire-suppressing components, hydrophobic ingredients, and inert fillers. During the fire extinguishing process, dry powder is propelled through dry powder storage tanks, driving gas devices, and piping systems, and sprayed as a powder mist onto the fire source. It forms a covering layer on the surface of the flames, simultaneously playing multiple roles such as chemical suppression, oxygen isolation, and cooling asphyxiation, quickly controlling the fire and achieving extinguishment. However, after extinguishing with dry chemical fire extinguishing agents, powder residue may remain on the surface of equipment, requiring timely cleaning to prevent corrosion or other damage to the equipment.
The Application of Main Types of Fire Suppression Systems in Commercial Environments
Aerosol Fire Suppression System
Aerosol fire suppression system primarily use type s aerosol generating agents, which produce aerosols with fire-extinguishing efficacy to achieve the purpose of extinguishing fires. These systems are pipeline-free and have the advantages of easy installation, low maintenance costs, and being environmentally friendly.
Working Principle:
- Activation Response: Upon receiving a fire alarm signal, the aerosol generating agent is activated.
- Generation of Fire Suppression Gas: The agent rapidly produces aerosol fire suppression gas, which is released through nozzles and quickly covers and inundates the protected area.
Fire Extinguishing Mechanism:
- Chemical Extinguishing: Metal salt particles in the aerosol absorb heat at high temperatures, reducing the flame temperature and suppressing the combustion reaction.
- Chemical Inhibition: Vaporized metal ions react with active groups in the combustion process, reducing free radicals.
- Solid-Phase Chemical Inhibition: Particles adsorb active groups, consuming them and decreasing the combustion rate.
- Asphyxiation: N2 and CO2 lower the oxygen concentration, aiding in fire extinguishing, but their effect is secondary compared to chemical inhibition and heat absorption cooling.
This system primarily relies on efficient chemical extinguishing, supplemented by physical heat absorption and asphyxiation, to achieve a rapid and environmentally friendly fire extinguishing effect.
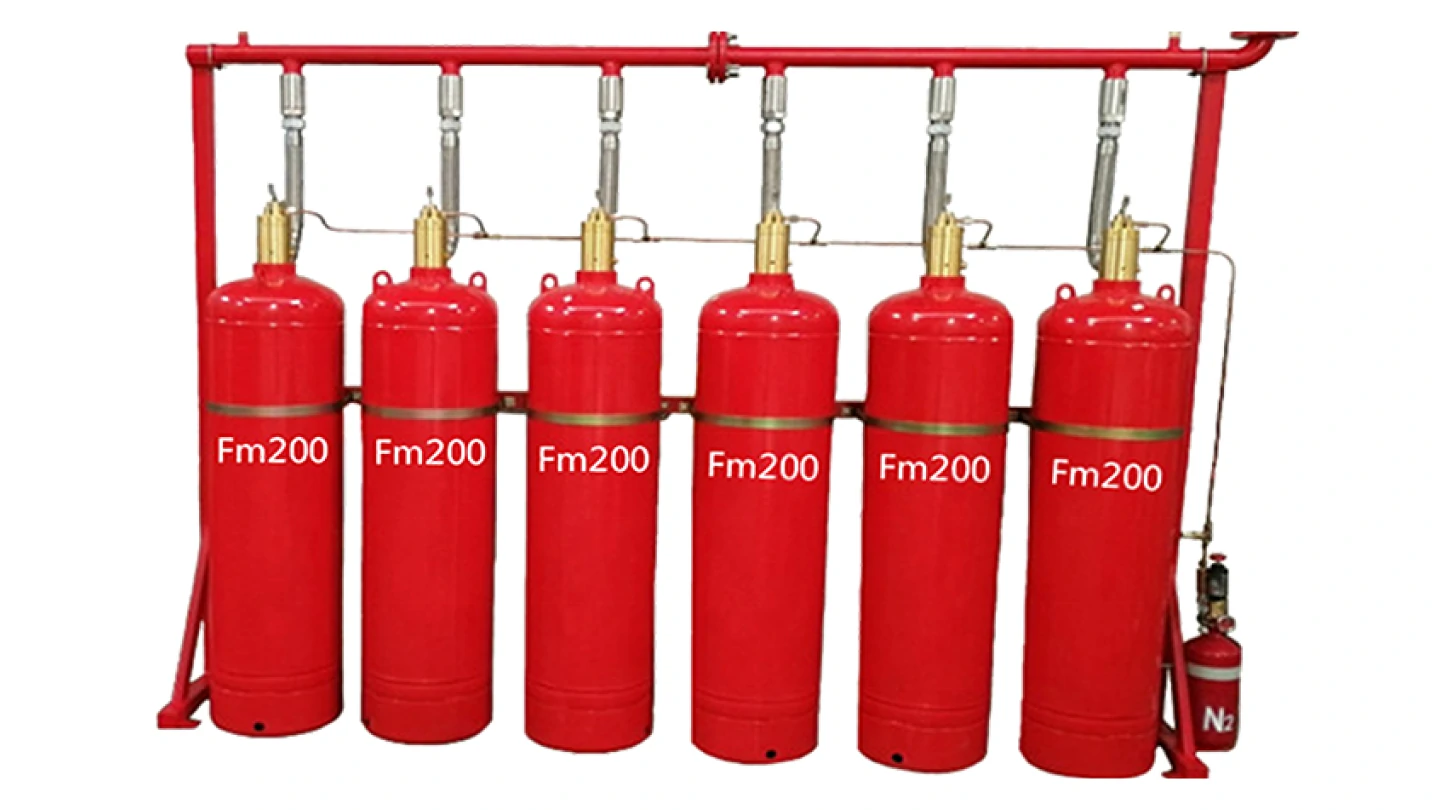
Gas fire suppression systems work by releasing specific gaseous fire suppressants to inhibit fires. These gases can be inert gases (CO2, nitrogen,Ig 100, argon) or chemically synthesized gases (FM200, Novec1230). The system is designed to quickly reduce the oxygen concentration or chemically suppress combustion reactions during a fire, thereby achieving the effect of extinguishing the fire.
Gas fire suppression systems achieve fire control through the following steps:
- Fire detection: Automatic detection of fire conditions using smoke, flame, or temperature detectors.
- Alarm confirmation: The detectors issue an alarm that requires manual confirmation before the system is activated.
- Initiate release: After confirming the fire, the gas fire suppressant is automatically or manually released.
- Gas release: The fire suppressant is transported through the pipeline system to the fire area, either directly or through a distribution method.
- Fire extinguishing effect: Fire is extinguished by reducing oxygen concentration, chemical suppression, and cooling effects.
- System monitoring: Continuous monitoring after release to ensure the fire is completely extinguished.
- Ventilation: After the fire is controlled, ventilation is carried out to expel harmful gases and ensure personnel safety.
Gas fire suppression systems are known for their high efficiency, speed, and lack of pollution, making them suitable for various locations, especially effective for fire suppression around electrical equipment.
CO2 Fire Suppression System
CO2 fire suppression system is fire protection systems that use carbon dioxide as the extinguishing agent, achieving the effect of suffocating fires by reducing the oxygen content in the space. Carbon dioxide is an inert gas that is inexpensive and does not pollute the fire scene when used for extinguishing; it dissipates quickly and leaves no residue after extinguishing. These systems are suitable for unoccupied areas because carbon dioxide can be suffocating to humans. Appropriate safety measures should be taken to ensure the safety of personnel when installed in places where people work regularly.
The system displaces oxygen, preventing the fire from continuing. Carbon dioxide systems are very useful when water could damage sensitive equipment or exacerbate the fire, such as in electrical fires in data centers.
Although effective, high concentrations of carbon dioxide can be harmful to humans, so sufficient safety measures must be taken when using it.
Working Principle of Carbon Dioxide Fire Suppression Systems
- Fire Detection: The system automatically detects fire conditions through smoke, flame, or temperature detectors.
- Initiate Release: After the fire is confirmed, the system is automatically or manually activated to release carbon dioxide.
- Gas Release: High-pressure stored carbon dioxide rapidly expands and absorbs heat, reducing the temperature at the fire scene while also reducing the oxygen concentration, achieving suffocating fire extinguishing.
- Fire Extinguishing Effect: Carbon dioxide is denser than air, covering the surface of the combustibles, isolating oxygen, and suffocating the flames.
- System Monitoring: The system automatically monitors the fire conditions to ensure the fire is completely extinguished.
When using carbon dioxide fire suppression systems, it is important to be aware of the asphyxiation risks of carbon dioxide, ensure the safe evacuation of personnel, and take appropriate protective measures in occupied areas.
Clean agent fire suppression system
Clean agent fire suppression systems, also known as gas fire suppression systems or clean agent gas fire suppression systems, are fire protection systems that use chemical clean agents or inert gases as fire-extinguishing media. These systems are primarily used to protect equipment and items that are sensitive to water or other traditional fire-extinguishing agents, such as data centers, archives, museums, libraries, and telecommunications equipment rooms.
Clean agent fire suppression systems achieve fire extinguishment mainly through the following methods:
- Physical action: By rapidly absorbing heat to reduce the flame temperature and suppress the fire. For example, FM-200 (heptafluoropropane) can rapidly cool the flame temperature during the molecular vaporization phase.
- Chemical suppression: Releasing free radicals during the chemical reaction process to prevent the chain reaction of combustion. FM-200 clean gas fire suppressant can release free radicals during the chemical reaction process, preventing the combustion chain reaction.
- Oxygen reduction: Suppressing fires by displacing heat and being located near the protected area, reducing the oxygen in the flame area. For instance, inert gas clean agent fire suppression systems use a combination of inert gases to reduce oxygen in the flame area when discharged.
- Total flooding system: Systems working on the principle of total flooding apply the fire suppressant to a three-dimensional enclosed space to achieve a concentration sufficient for extinguishing the fire.
- Local application system: Directly spraying the fire suppressant onto the fire (usually a two-dimensional area) or directly into the three-dimensional area surrounding the combustible material or object.
- Room Integrity Test (RIT): Ensuring that the room is sealed enough to ensure the effectiveness of the fire suppression system in the event of a fire. The RIT works by creating pressure in a room or enclosure where the fire suppression system is installed, ensuring that the gas does not escape too quickly from the room to extinguish the fire.
Clean agent fire suppression systems are widely used in various fire scenarios due to their high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and cost-effectiveness, especially in situations requiring a rapid response and clean fire-extinguishing agents. However, due to their potential dangers, the design, installation, and maintenance of the systems must strictly adhere to relevant standards and regulations.
Water-based Fire Suppression Systems
Water-based fire suppression systems are fire protection systems that primarily use water as the fire-extinguishing agent and are widely used to extinguish fires involving solid combustibles such as wood, paper, and fabric. These systems are simple, economical, safe, and environmentally friendly, suitable for a variety of settings including homes, industries, businesses, and public spaces.
Water-based fire suppression systems are mainly divided into two types: automatic sprinkler systems and fine water mist systems.
Automatic sprinkler systems are commonly seen in commercial and residential facilities, known for their simplicity, reliability, and economic feasibility. Composed of multiple components, the system’s pipes are filled with pressurized water, which is released immediately when the sprinkler heads activate in the event of a fire.
Fine water mist systems release tiny water droplets that cover a larger surface area. The mist produced helps to rapidly absorb heat, create a cooling effect, and prevent the spread of the fire. Its unique design and functionality make it an ideal choice for spaces where water damage must be avoided.
Water-based fire suppression systems are widely used in various fire scenarios due to their environmentally friendly, efficient, and economical characteristics. However, it is important to note that water-based fire suppression systems are more effective in extinguishing solid fires, and their effectiveness may be poor, or even contribute to the spread of the fire, when used on fires involving non-water-soluble oils, fats, or metal fires.
Foam Fire Suppression Systems
Foam fire suppression systems are firefighting systems specifically designed to extinguish fires involving combustible liquids. They work by generating a large amount of foam to cover the surface of the burning liquid, isolating oxygen, reducing temperature, and suppressing the spread of the fire. These systems are widely used in places with flammable liquids, such as oil refineries, chemical plants, oil storage facilities, and ports.
Foam fire suppression systems combine water, foam concentrate, and air to create a foam layer that can cool the fire, isolate the flame from the fuel source, and quickly spread to cover the fire, preventing oxygen from entering and preventing re-ignition. They are commonly used in industrial settings such as hangars and fuel storage facilities.
The working process involves preparing the foam solution (a mixture of water, stabilizers, and foaming agents), providing pressure, transporting it to the nozzles to mix with air and form stable foam, and then covering the surface of the combustibles, isolating oxygen, and blocking heat transfer to control and extinguish the fire.
Chemical Fire Suppression Systems
Chemical fire suppression systems work by using chemical agents to interrupt the chemical reactions during a fire, breaking the combustion cycle. These systems are mainly divided into two categories: wet chemical and dry chemical.
Wet Chemical Systems: Wet chemical systems use wet chemical solutions to extinguish fires, suitable for kitchen grease fires. Upon activation, the system releases a fine mist that cools the fire and forms a foam layer to deprive the fire of oxygen, achieving the fire-extinguishing effect. When the wet chemical fire suppressant is sprayed onto the burning cookware, it cools the grease and saponifies with the high-temperature grease to form a saponification membrane that cuts off the fire’s contact with oxygen until the grease cools below the ignition point, preventing re-ignition.
Dry Chemical Fire Suppression Systems: Dry chemical fire suppression systems use powder fire extinguishing agents, which are composed of various fine inorganic powders. The particle size and distribution affect the fire-extinguishing effectiveness. During extinguishing, the powder mist mixes with the flame, providing chemical suppression, isolation, cooling, and suffocation effects. Due to their multifunctionality, they are popular in industrial settings and vehicle applications, capable of quickly extinguishing fires and protecting equipment. They are harmless to humans and the environment and are considered environmentally friendly.
What is the role of fire suppression systems in modern society?
Fire suppression systems occupy a central position in the fire safety framework of modern society, demonstrating multidimensional importance in their role.
Firstly, in terms of enhancing fire prevention and extinguishing efficiency, fire suppression systems leverage advanced detection technologies, efficient activation mechanisms, and precise suppressant release systems to respond rapidly at the moment a fire occurs. This timely initiation of fire extinguishing procedures effectively curtails the spread and escalation of the fire, thereby better protecting people’s lives and property.
In terms of compliance with regulations and industry standards, fire suppression systems play an indispensable role. Many countries and regions have laws and regulations that explicitly require certain types of premises, such as high-rise buildings, densely populated areas, and storage facilities for flammable and explosive hazardous chemicals, to install fire suppression systems that meet corresponding standards by law.
On the level of social stability and public safety, fire suppression systems, as a core component of public fire protection efforts, play an irreplaceable role in maintaining social order and ensuring public safety.
Under the trend of technological innovation and intelligence, fire suppression systems have made a qualitative leap with the help of cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and artificial intelligence.
In the fields of environmental protection and cultural heritage preservation, the appropriate selection and application of fire suppression systems hold vital significance. As societal awareness of environmental and cultural heritage protection continues to grow, waterless fire suppression systems, such as gas fire suppression systems and dry chemical fire suppression systems, are increasingly being adopted due to their unique fire-extinguishing characteristics and environmental friendliness.
The development and application of fire suppression systems have not only enhanced the capability of fire prevention and control but also provided significant protection for the stability and development of society. With the advancement of technology, fire suppression systems will continue to play an increasingly vital role in safeguarding people’s lives and property.
Where is a fire suppression system needed?
In spaces where there is a high risk of fire or potential for catastrophic losses, fire suppression systems are extremely important. Fire suppression systems are particularly crucial in the following situations and venues:
- High-rise Buildings and Commercial Facilities: Automatic sprinkler systems and gas fire suppression systems are used for fire prevention and control, protecting the safety of personnel and structures.
- Industrial and Manufacturing Sites: Foam fire suppression systems, dry chemical fire suppression systems, and gas fire suppression systems provide comprehensive protection for factory fire safety, safeguarding employees and equipment.
- Storage Facilities: A combination of automatic sprinkler systems and smoke alarm systems allows for a rapid response to fires, reducing the loss of goods.
- Catering Industry: Wet chemical fire suppression systems effectively address kitchen grease fires.
- Data Centers and Telecommunications Facilities: FM-200 clean agent fire suppression systems protect digital assets and critical infrastructure, quickly extinguishing fires without damaging electronic equipment.
- Medical Institutions: Gas fire suppression systems ensure the safety of patients and the protection of medical equipment.
- Vehicles: Oil tankers and chemical transport vehicles are equipped with dry powder or foam fire suppression systems to promptly extinguish fires.
- Cultural Heritage Protection: Carbon dioxide gas fire suppression systems protect valuable cultural relics and materials, avoiding damage from water or foam.
- Special Equipment Rooms: Carbon dioxide fire suppression systems are suitable for high-temperature, high-pressure environments such as oil pipeline pump stations, quickly suppressing fires.
- Places with Strict Environmental and Equipment Requirements: Perfluorinated ketone fire suppression systems are suitable for electronic chip manufacturing workshops, leaving no residue and causing no harm to equipment and products.
Fire suppression systems come in a variety of types, each with its unique application scenarios and advantages. In practical applications, we need to choose the appropriate fire suppression system based on specific fire risks and scenarios, and regularly perform maintenance and inspections to ensure that they can function effectively at critical moments.
In summary, fire suppression systems are essential tools for protecting people’s lives and property, maintaining social stability, and promoting economic development. As society progresses and technology advances, fire suppression systems will continue to play an increasingly vital role in fire prevention and emergency response.